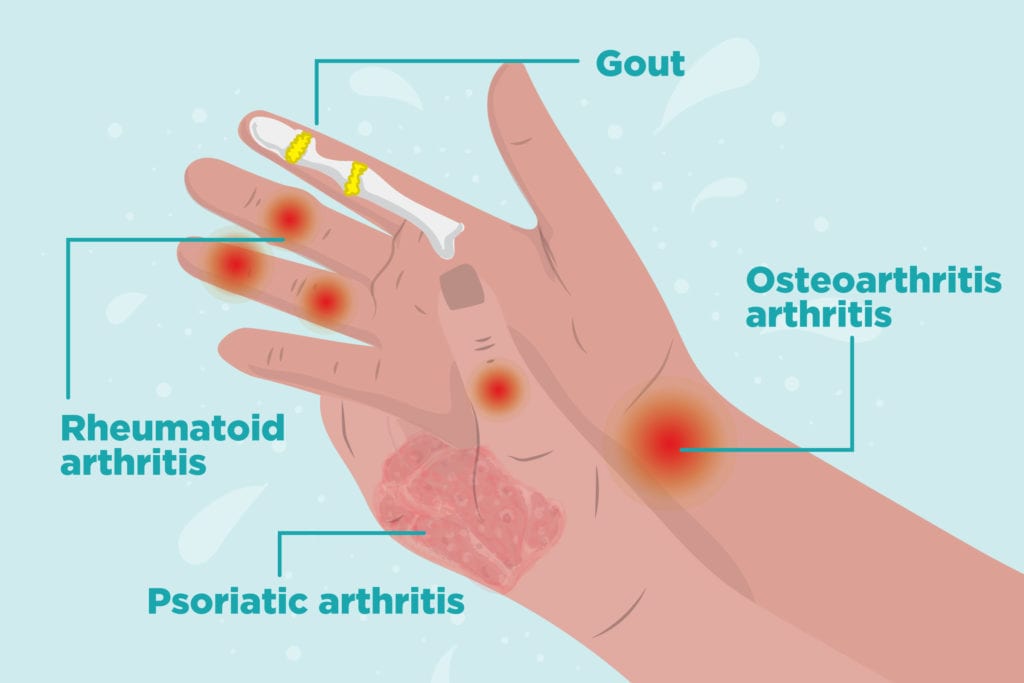
The symptoms of arthritis, depending on the type, can develop gradually or suddenly. As arthritis is most often a chronic disease, symptoms may come and go, or persist over time.
However, anyone who experiences any of the following four key warning signs should see a doctor.
- Pain:Pain from arthritis can be constant, or it may come and go. It may affect only one part or be felt in many parts of the body.
- Swelling:In some types of arthritis, the skin over the affected joint becomes red and swollen and feels warm to the touch.
- Stiffness:Stiffness is a typical symptom. With some types, this is most likely upon waking up in the morning, after sitting at a desk, or after sitting in a car for a long time. With other types, stiffness may occur after exercise, or it may be persistent.
- Difficulty moving a joint:If moving a joint or getting up from a chair is hard or painful, this could indicate arthritis or another joint problem.
In addition to these general signs, certain types of arthritis may cause their own unique symptoms. For example, Juvenile RA can cause eye problems, including uveitis, iridocyclitis, or iritis.
Septic arthritis often causes fever and intense joint pain. It can become an emergency if it progresses to sepsis.
Causes of arthritis
There is no single cause of all types of arthritis. The cause or causes vary according to the type or form of arthritis.
Possible causes may include:
- an injury, which can lead to degenerative arthritis
- an abnormal metabolism, which can cause gout and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD)
- a genetic inheritance, which can lead to developing osteoarthritis
- an infection such as Lyme disease, which can trigger arthritis symptoms
- an immune system dysfunction, such as the type that causes RA and lupus
Most types of arthritis are linked to a combination of factors. However, some have no obvious cause and appear to be unpredictable in their emergence.
Treatment of arthritis
Treatment for arthritis aims to control pain, minimize joint damage, and improve or maintain function and quality of life. A range of medications and lifestyle strategies can help achieve this and protect joints from further damage.
The exact treatment depends on the type of arthritis a person develops. It may involve:
Medication
Medications will depend on the type of arthritis. Commonly used drugs include:
- Analgesics: These reduce pain. However, they have no effect on inflammation. Examples include acetaminophen (Tylenol) and tramadol (Ultram).
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These reduce both pain and inflammation. NSAIDs include available to purchase over-the-counter or online, including ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB) and naproxen sodium (Aleve). Some NSAIDs are available as creams, gels, or patches which can be applied to specific joints.
- Counterirritants: Some creams and ointments contain menthol or capsaicin, the ingredient that makes hot peppers spicy. Rubbing these on the skin over a painful joint can modulate pain signals from the joint and lessen pain.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): These are used to treat RA. DMARDs slow or stop the immune system from attacking the joints. Examples include methotrexate (Trexall) and hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil).
- Biologics: These are genetically engineered drugs that target various protein molecules involved in the immune response. Examples include entanercept (Enbrel) and infliximab (Remicade).
- Corticosteroids: prednisone and cortisone reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.
Natural remedies
A healthful, balanced diet, along with appropriate exercise and avoidance of smoking and drinking too much alcohol can help people with arthritis maintain their overall health and reduce symptom severity.
Diet
Eating some types of food may help reduce inflammation.
The following foods, found in a Mediterranean diet, can provide many nutrients that are good for joint health and can help relieve joint inflammation.
- fish
- nuts and seeds
- fruits and vegetables
- beans
- olive oil
- whole grains
On the other hand, people living with arthritis should avoid or limit eating processed foods, foods that contain added sugar, and refined carbohydrates. These foods may actually make arthritis inflammation worse.
Physical therapy and exercise
Doctors will often recommend a course of physical therapy to help patients with arthritis overcome some of the challenges and to reduce limitations on mobility.
Forms of physical therapy that may be recommended include:
- Physical therapy: specific exercises tailored to the condition and individual needs, sometimes combined with pain-relieving treatments such as ice or hot packs and massage
- Occupational therapy: practical advice on managing everyday tasks, choosing specialized aids and equipment, protecting the joints from further damage, and managing fatigue
In addition, although individuals with arthritis may experience short-term increases in pain when first beginning exercise, continued physical activity can effectively reduce long-term symptoms.
People with arthritis can participate in joint-friendly physical activity on their own or with friends. As many people with arthritis have other conditions, such as heart disease, it is important to choose appropriate activities.
Joint-friendly physical activities that are appropriate for adults with arthritis and heart disease include:
- walking
- swimming
- cycling
A healthcare professional can help you find ways to live a healthful lifestyle and have a better quality of life.
Herbal medicines
A number of natural remedies have been suggested for different types of arthritis. Research Trusted Source has shown that some herbal supplement may be able to relieve some pain and inflammation or help reduce the need for taking pain medications. These include:
- Devil’s claw
- Boswellia
- chamomile
- turmeric
- ginger
However, anyone considering using natural remedies for any type of arthritis should speak to a doctor first.
Surgery
Depending on the type of arthritis a person has, different surgical treatments on the affected joints may be necessary. It may depend on the degree of a person’s symptoms and whether other treatments have been successful.
Surgery options for arthritis include:
- synovectomy
- total joint replacement (TJR)
- osteotomy
- joint fusion